The CISSP qualification
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification has become a prerequisite for anyone developing a senior career in information security. It provides information security professionals with an objective measure of competence and a globally recognized standard of achievement. The CISSP credential suits mid- and senior-level managers who are working towards, or have already attained, positions such as CISO, CSO or senior security engineer.
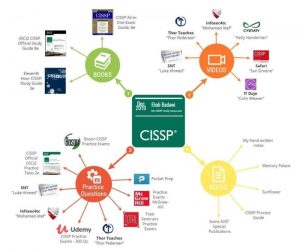
Path to passing the CISSP examination at one attempt: Here is a collection of resources that have helped previous CISSP test takers pass the test at one attempt
How to qualify for the CISSP certification
To qualify for the CISSP certification, you must:
- Have a minimum of five years’ experience in two or more of the eight CBK domains.
- Pass the CISSP examination.
- Complete the endorsement process and subscribe to the (ISC)² Code of Ethics.
- Maintain certification through continuing professional education (CPE) credits.
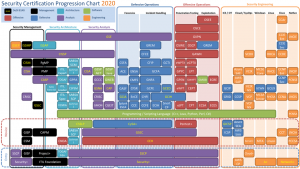
CISSP CBK
CISSP was developed and is maintained by (ISC)², the International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium. At the heart of CISSP is an information security common body of knowledge (CBK), which is divided into eight domains:
- Security and Risk Management
- Asset Security
- Security Engineering
- Communications and Network Security
- Identity and Access Management
- Security Assessment and Testing
- Security Operations
- Software Development Security
The Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK is the essential guide for those preparing for the CISSP exam.
Who Earns The CISSP?
According to the official ISC2 website, CISSP is ideal for experienced security practitioners, managers, and executives interested in proving their knowledge across a wide array of security practices and principles, including those in the following positions:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- Chief Information Officer (CIO)
- Director of Security
- IT Director/Manager
- Security Systems Engineer
- Security Analyst
- Security Manager
- Security Auditor
- Security Architect
- Security Consultant
- Network Architect